How to assess knowledge building?
From Teacher Assessment to Student Assessment - Assessment for Learning
Page Outline
Quantitative Assessment- The use of Analytic Toolkit (ATK)
- The use of Applets Assessment Tools
- Self and peer assessment
- Learning diary
- Portfolio note
Assessment for Learning
Assessment for learning is advocated as one of the important features in the education reform. Knowledge building is one of the highest forms of assessment for learning as students constantly reflect on their changing states of learning, which serve as the basis for the continuous improvement of ideas.Although knowledge building possesses the nature of assessment for learning, teachers may still like to know about the strategies to assess knowledge building, both quantitatively and qualitatively.

Quantitative assessment
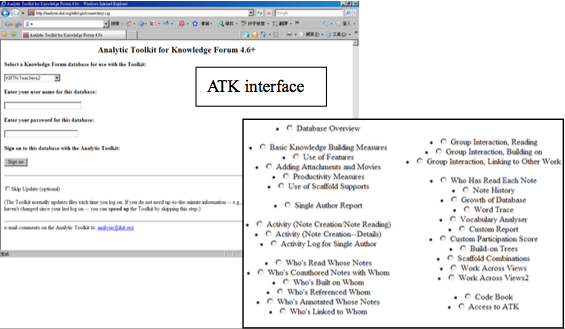
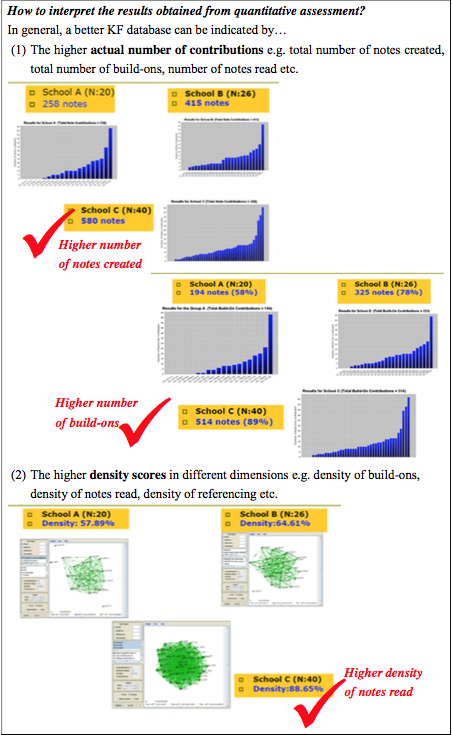
1. The use of the Analytic Toolkit (ATK)
- It is an online tool (available at http://analysis.ikit.org) which helps teachers generate various types of participation scores for students.
- ATK provides various kinds of quantitative measures to analyze students’ performance on KF
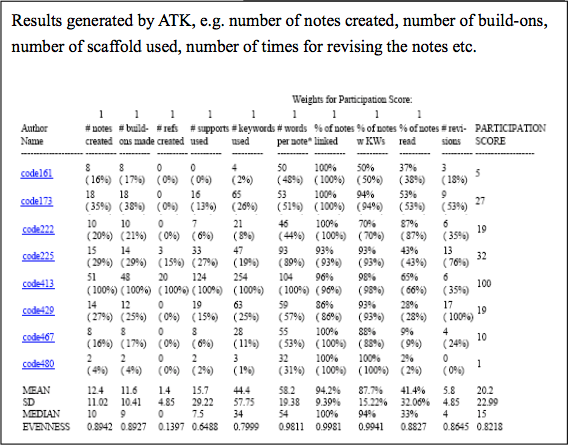
2. The use of Applets Assessment Tools
- Applets assessment tools are directly available in KF
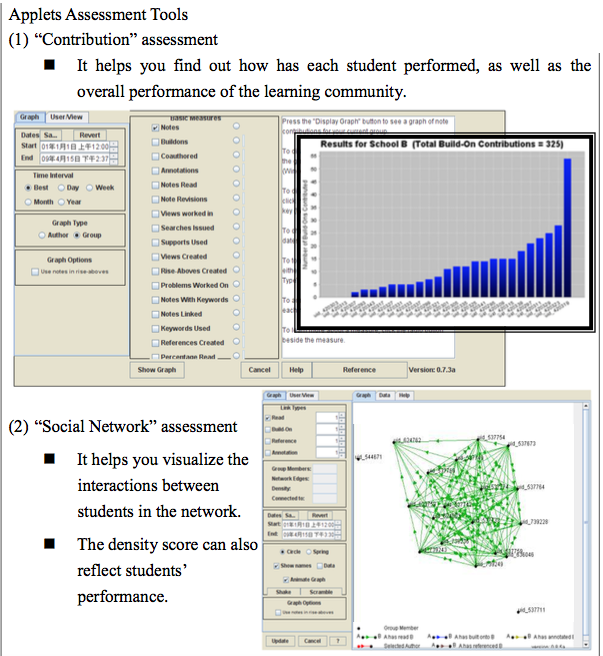
- They help to measure individual students’ performance in KF and also the overall performance of the learning community
- Two most frequently used tools are ‘Contribution’ and ‘Social network’.
- ‘Vocabulary Growth’ is useful especially for language subjects.
2. Qualitative assessment
1. Self and Peer assessment
Self assessment and peer assessment are powerful qualitative assessment methods.
- Peer assessment is particularly effective for
- Increasing students’ motivation to discuss and learn
- Helping students review and learn from the works of other
- Helping students reflect more holistically on the collaborative knowledge building process of the whole community
- Teachers may ask students to work in groups to
- Summarize the KF discussion done by another group
- Evaluate the quality of the discussion on various dimensions (e.g. quality of the ideas proposed, scaffolds used, questions raised, arguments used, new ideas generated, reference cited etc.)
- Provide suggestions for improvement
- Present the above in class
2. Learning diary
- Students write notes that records thoughts and insights about students’ own learning experience
- It encourages students to:
- review and consolidate learning,
- evaluate performance and gain insight of their own strengths and weaknesses as learners
- plan future learning (and overcoming learning difficulties) based on past learning experience.
- take charge of their own learning, and to develop into independent life-long learners.
- Teachers may provide scaffolds, rubrics and guidelines to facilitate student’s reflective journal writing

- Teachers may provide some generic prompting questions, such as
- What have you learnt about topic ‘X’?
- Why the referenced notes are important to your understanding of topic ‘X’?
- These generic questions provide students the greatest freedom to ponder upon things that had the greatest personal significance
3. Portfolio note
- By writing summary notes/ portfolio notes, students can
- analyze the inter-relatedness of the community’s ideas
- reflect on the knowledge building process that the learning community have gone through
- Teachers may
- use classroom KB talk to facilitate students’ reflection on their own inquiry process
- let students discuss on the criteria for good notes and good discussion
- ask each student to write a portfolio note to reflect on the discussion and their own learning,
- or assign seed students to be responsible for writing summary notes for different parts of the discussion (e.g. different phases, different subtopics)
- Referencing, rise-above note and workspace are all useful aids which help the writing of summary/portfolio notes

