Background
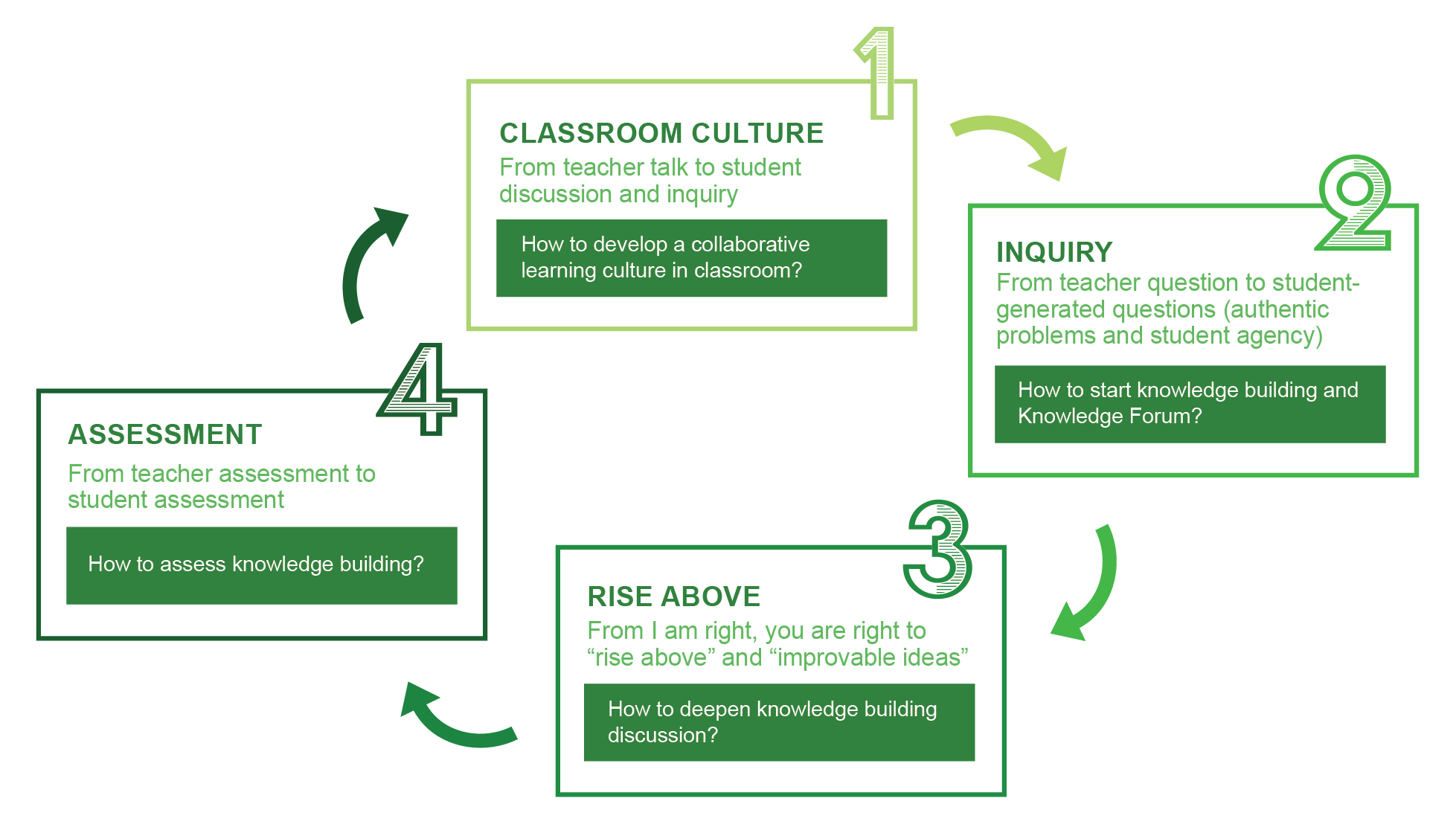
How to conduct knowledge building in classroom?
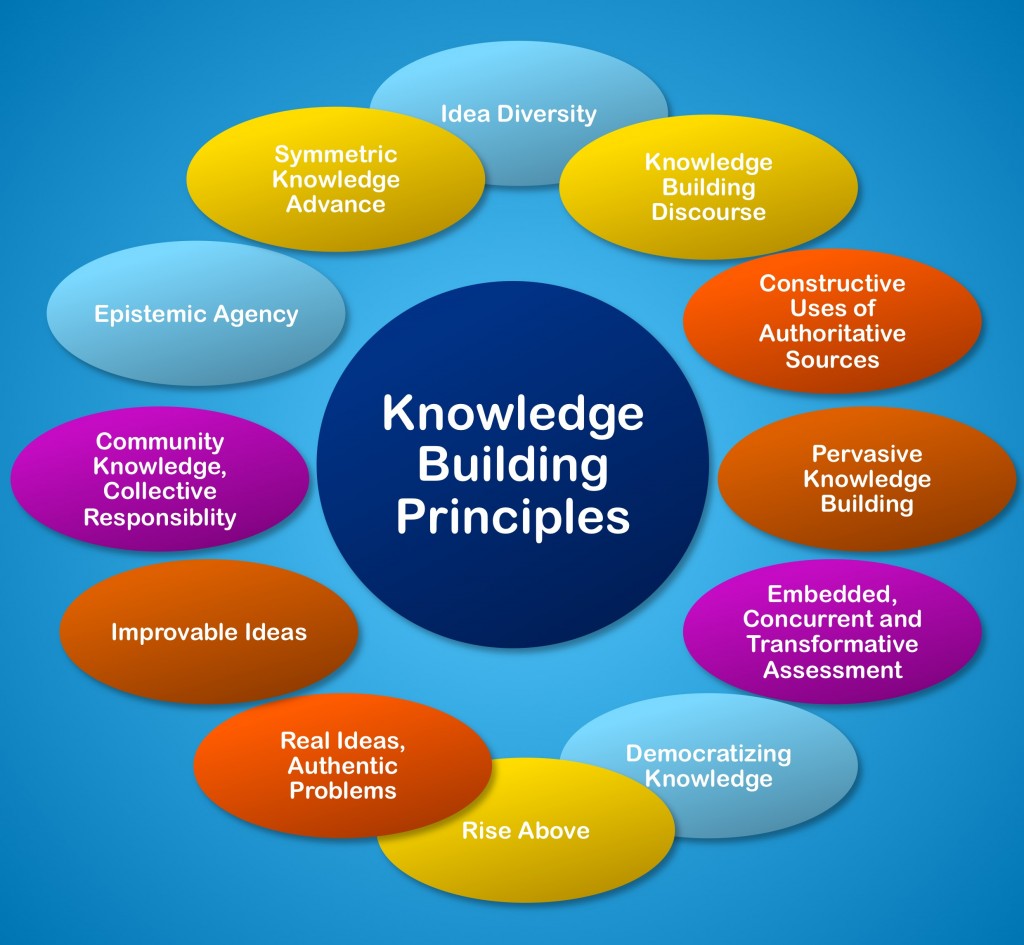
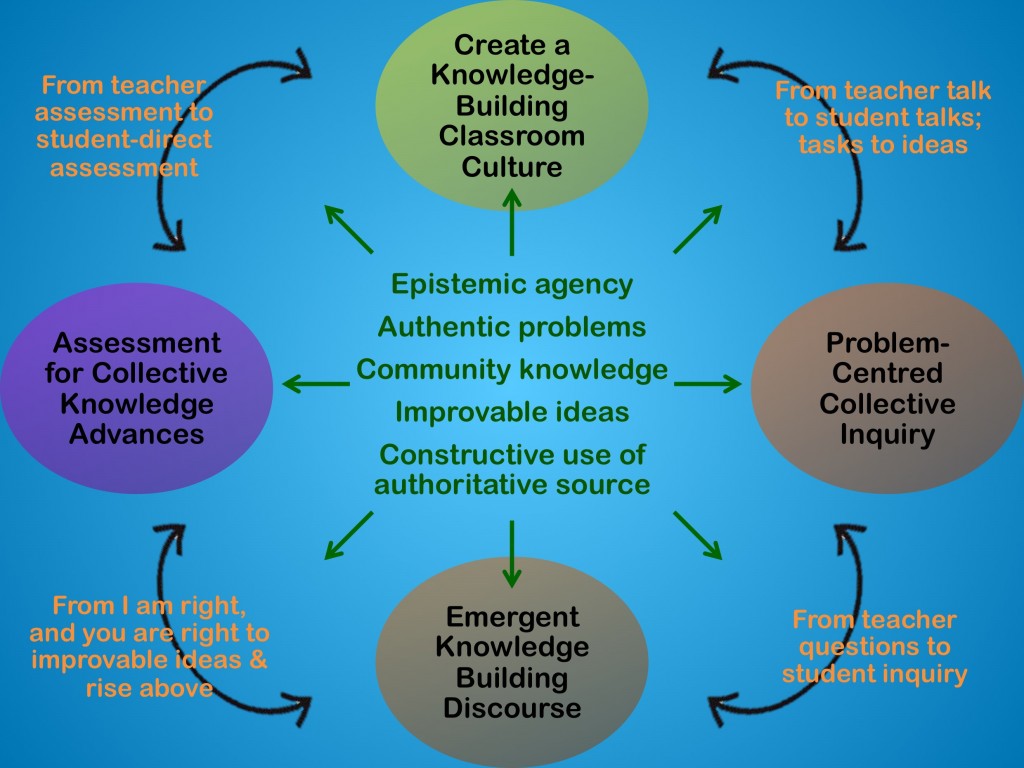
Knowledge Building Principles
- Real ideas, authentic problems (relevant to daily life) 討論投入 聯繫現實
- Epistemic Agency (active learning and ownership) 追求知識 自主自力
- Idea diversity (multiple-perspectives) 多元觀點 正反並現
- Community knowledge (team building and collective benefit) 共同承擔 知識無限
- Improvable ideas (continuous improvement) 不斷鑽研 完善觀點
- Rise above (deepening) 融會總結 昇華超越
- Constructive Use of Authoritative Sources (use of information) 善用權威 助己發揮
- Democratizing knowledge (catering for individual difference) 知識面前 平等參建
- Embedded and transformative assessment (assessment for learning) 時刻反思 改進認知
- Knowledge building discourse (productive discussion/ inquiry) 討論交流 建構為優
- Symmetric knowledge advancement (win-win situation ) 跨組參詳 並行成長
- Pervasive knowledge building (different subjects/ inside-outside school) 知識建構 無處不透
Major principles are: epistemic agency, improvable ideas and community knowledge Q: How does knowledge building take place in classroom? A: Start by developing a knowledge building culture in classroom, such as:
- Make ideas public and visible for improvement (by using poster idea cards, knowledge walls)
- Students continue to engage on collective inquiry after formulating problems and theories, supported by knowledge forum
- Students reflect and assess one another’s ideas, conduct experiments to test hypotheses and construct explanations
Example & Explanation
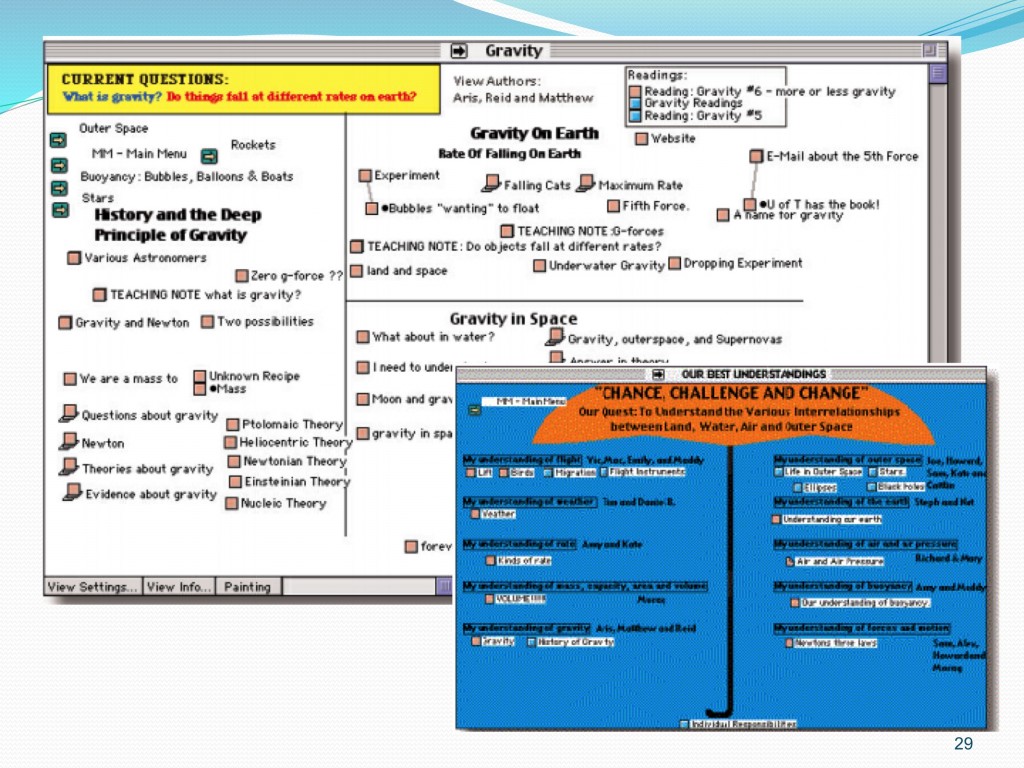
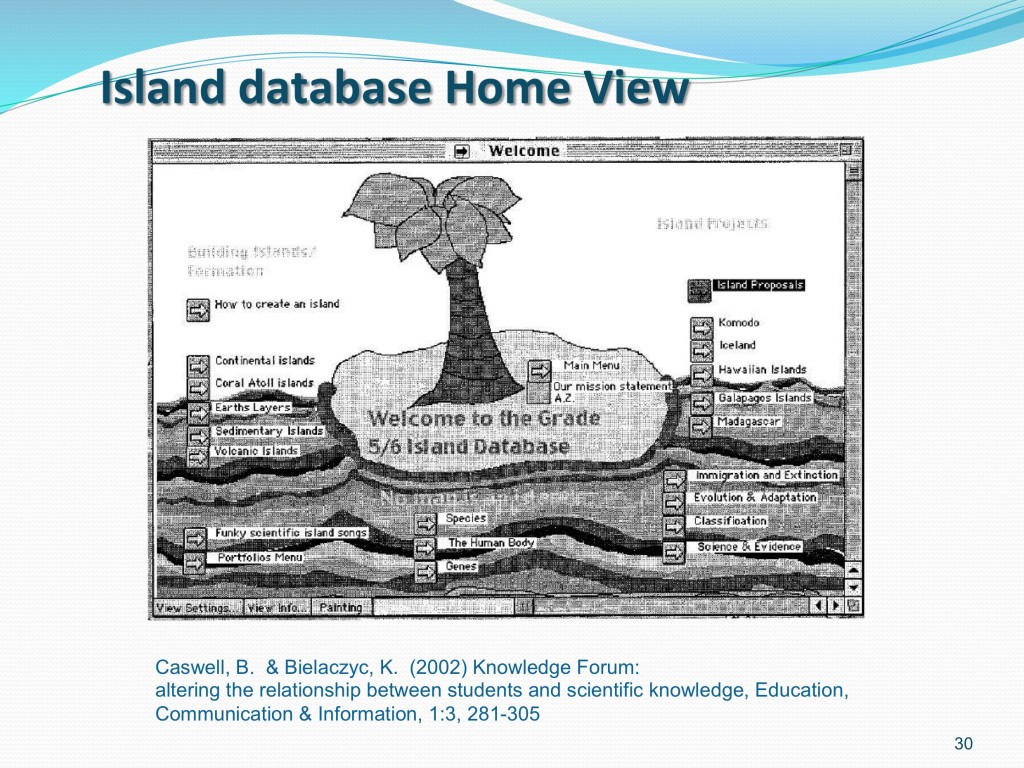
An example of knowledge building classroom in Toronto
Classroom Processes of Knowledge Building in Toronto Classrooms
- Specify curriculum and learning goals as well as encourage students' self-directed inquiry; design underpinned with knowledge building principles
- Inquiry time, typically a single period each day of the week, with student questions leading the inquiry
- Students worked for about 30 minutes, reading, writing and reflecting on notes on Knowledge Forum
- Students worked individually or in small groups reading resources, conducting experiments brought in by teachers and students
- In whole-class, knowledge-building talk, students brought problems of understanding and knowledge advances they found in Knowledge Forum
Summary
Principle-Based Pedagogy
Principles-Based Pedagogy